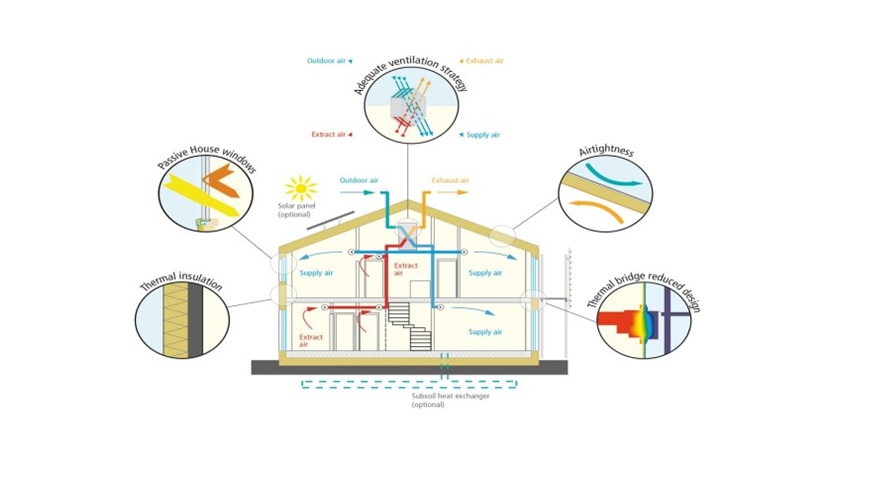
Passive house is a concept used in construction to build environmentally friendly, comfortable and energy-efficient buildings, and these buildings can also be affordable. It is a building standard composed of many design principles that are used to achieve precise energy efficiency levels with a certain degree of comfort. Passive houses can effectively use sunlight, internal heat sources and heat recovery, even in the coldest seasons without the need for a typical heating system. In addition to some cooling methods (for example, summer strategies), the temperature can also be kept within a comfortable range.
Principle of Passive House Design:
Insulation:
The insulation of the building minimizes heat loss in the colder months and keeps your home cool in the warmer months. Ceilings, walls and floors need to be insulated. The material used for insulation forms a barrier between indoor and outdoor spaces. It is essential in both hot and cold climates, because it can significantly reduce the energy consumption of traditional heating and cooling systems and create a comfortable indoor temperature throughout the year. It can be used to build passive houses, such as cellulose, cotton, lamb wool, glass fibre, polyurethane, rock wool, etc.
High-Quality Doors and Windows:
Doors and windows play an important role in the design of passive houses. It is necessary to use the highest quality doors and windows that have low thermal conductivity and provide the best thermal insulation, because they provide light and visibility and cannot be insulated in them. Similar to a wall, it becomes a weak link in terms of thermal resistance. Therefore, high-quality doors and windows that meet the passive house standards must be used.
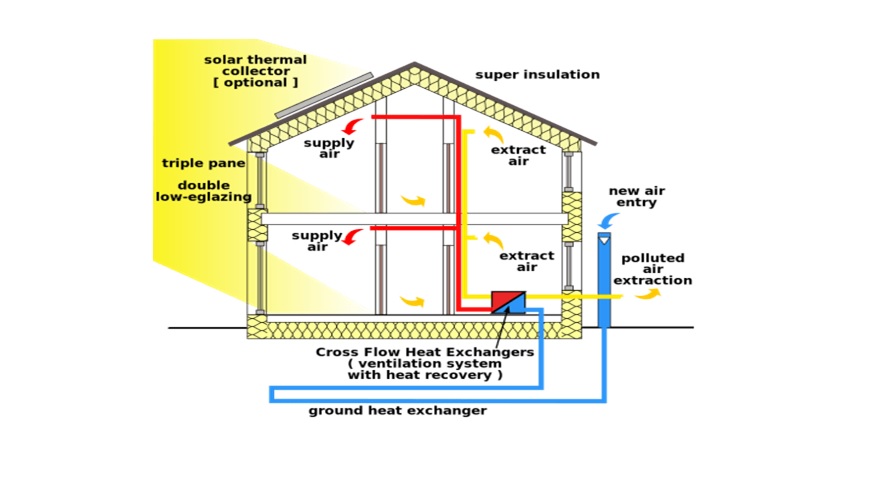
Heat Exchange in a Passive House
Airtightness:
During the construction of a passive house, the building is sealed to control unnecessary air flow, thereby avoiding hot air leakage or cold air infiltration. To be certified as a passive house, a building must attain the standard of 0.6 ach-1 @ 50 Pa. This means that if the air pressure difference between the inside and outside of the house is 50 Pa, the air exchange volume per square meter of building area per hour should be less than 0.6 cubic meters.
Thermal Bridge Free Detailing:
Another principle of passive house construction is to minimize thermal bridges, which are the meeting points of various architectural details in the building. How do windows connect to the wall or how the wall connects to the balcony or how the wall meets at the corner? The purpose is to avoid the formation of cold bridges, which may cause heat dissipation and increase the risk of condensation by creating local cold spots. There are several ways to avoid cold bridges. Measures such as changing the design of a typical building or reducing the direct conductive connection between the inside and the outside can be used to determine the effectiveness of the insulation used in passive houses.
Heat Recovery Ventilation:
Passive houses require a lot of ventilation because they are sealed, over-insulated, and use heat recovery ventilation devices. The system aims to reduce energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and overall heating costs. Place and use a heat exchanger to absorb heat from the warm air in the room and transfer it to the cold air. This allows fresh air to circulate indoors while maintaining the ideal temperature. The air does not mix, so the air entering the house remains hot and cold. The success rate of these systems is about 90%, and some can even run as low as 15 watts per hour.
Benefits of Passive House:
Energy Efficiency:
Passive houses should save energy first. Compared with the typical energy consumption of traditional buildings, its energy consumption is greatly reduced, and it can even save up to 90% of energy consumption, while still having the same or even better functions.
Eco-Friendliness:
In passive houses, even in the harshest climates, traditional heating and cooling systems are no longer needed. It uses the natural energy of the sun and wind without harming the environment or consuming precious energy.
Good Indoor Air Quality:
Passive houses have a special ventilation system that can draw out air from the kitchen, bathroom and other areas that release moisture or odor, and introduce fresh air into bedrooms and other living areas. It also helps to control dust and keep indoor air fresh and clean.
Affordability:
Although the cost of constructing a passive house is usually 10% higher than that of a traditional house, the labour and maintenance costs are greatly reduced. Passive houses generate much less electricity bills.
Comfort:
Passive house design provides unparalleled indoor comfort, airtightness ensures good sound quality of the house, and the insulation layer prevents cold corners and excessive heat loss, while the temperature of the entire house remains uniform. Thus, the atmosphere inside a passive house remains pleasant and quiet.