Air conditioning will make architects lazy. Before its invention, many different methods had been used to cool and ventilate buildings. But why bother them when you can make an old box and put it in the air conditioner? In this way, there are 1.6 billion aviation units in operation in the world today. As the world warms, more people will want it. If air conditioners continue to grow at the current rate, they will reach 5.6 billion units by 2050. The irony is: we are eager to remain calm in a warming world. It can irreversibly change the weather. The following are some design principles for buildings with passive cooling characteristics
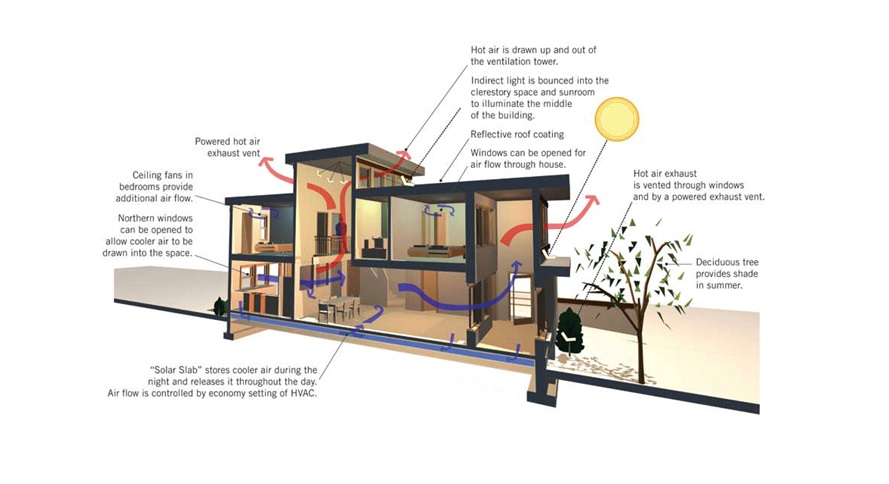
First, it is important to reduce the penetration of heat through the windows. The main problem with many houses is the sunlight shining from the windows all day long. If the same houses are built at different times, they will have shutters or brise-Soleil (France: Sun Breaker), a grille or an awning that covers the entire sun. These houses have deep porches or roofs that can protrude from windows and block shadows. The important thing is, strong summer sun will not shine directly and will not heat the interior.
It warms naturally but ventilation is the best way to deal with it. If you can open the windows on both sides of the house, you can ventilate the building and dissipate heat. Inner door-even if the door is closed, air can circulate. “Stack ventilation” in which hot air is exhausted from the windows through the roof cooler air is draw from the bottom. The air is below. Persian architects used shovels to enhance this effect. Today, we can use vents or automatic skylights, like active house does.
In hot countries, strategically planting shade trees or providing shade in other ways can greatly reduce cooling costs. Plant the trees to South and West of your house, when leaves fall, they will shade in summer, but will not block the light in winter.
Good heat insulation can keep your house warm in winter, but it can also prevent the house from overheating. In traditional Middle Eastern architecture, houses are built with thick walls to keep the interior cool. Some high-performance greenhouses have earth walls to solve this problem, so it provides insulated in winter and keep cool in summer. Thick walls or earth mounds also increase the thermal mass. Most materials (such as stone, concrete or soil) take a long time to heat or cool. This can help regulate the temperature. It heats up during the day and emits heat at night.
Equally important is the shape of the buildings and their orientation around each other so that the wind moves in a certain way. Homes built around courtyards have been popular for thousands of years in hot countries, often with a pond or a water feature in the middle to create air flow and evaporative cooling.