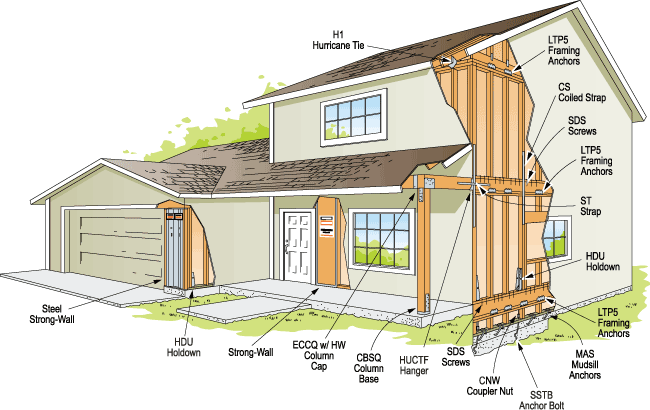
An earthquake is an unexpected and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the movement of the rocks below. The earth is strongly vibrated in all directions, which will generate inertial forces in the structure and cause loss of property and life. Therefore, understanding how to design earthquake-resistant structures, especially in earthquake-prone areas, can help reduce the impact of earthquakes.
The earthquake resistance of small structures can be increased by taking safety measures during the process of site selection, building planning, and construction.
- Site Selection: The structure must not be constructed on/around:
- Near unsafe embankments
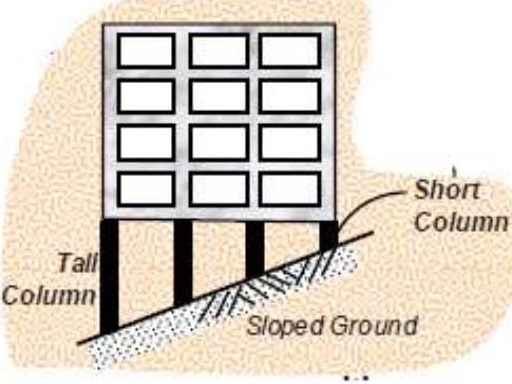
- Sloping ground with different height of columns
- Flood-impacted locations
- Subsoil with significant discontinuity like rock in some part, and soil in some area
- Structure Planning:
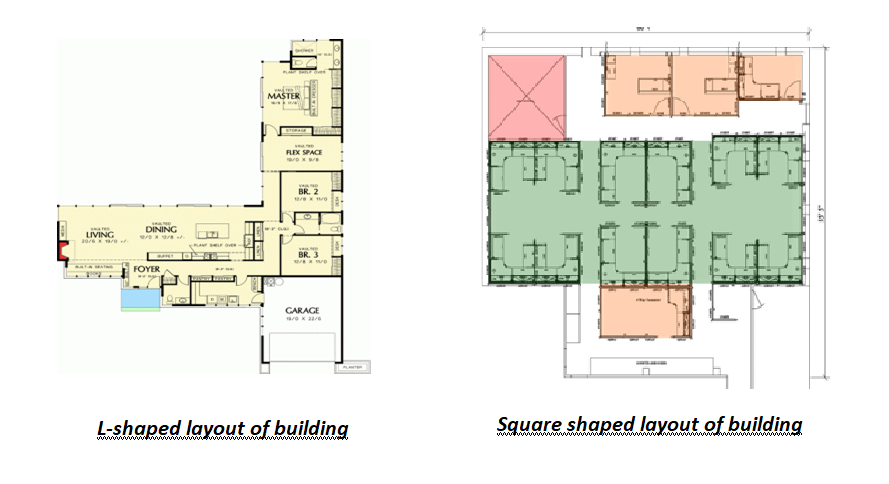
Symmetrical design is much safer than asymmetrical design. Therefore, the design should be square or rectangular instead of L, E, H, T – shaped. The length of the rectangular design should not exceed twice the width.
- Foundations:
The foundation width of a one-layer structure must be at least 700 mm, and the foundation width of a multi-layer structure must be at least 950 mm. For soft ground, the depth of the structure must be at least 1.0 m, and for rocky ground, the depth of the structure must be at least 0.45 m. When laying the foundation of the structure, all bulk material and water must be removed from the trench and compacted to the required height. After laying, fill the foundation and fill the backfilled soil.
- Masonry:
- In case of stone masonry
- Set each stone flat on its broadest face.
- Put the length of stones into the thickness of wall to guarantee interlocking with the inside and outside faces of the wall.
- Fill void spaces by utilizing little chips of stones with minimum possible mortar.
- The stone should not contain any rounded face; it should have angular faces only.
- Through stones should be use at least at vertical range of 600 to 750 mm.
- In case of brick masonry
- Properly burnt bricks with sharp edges should be used
- For making the most durable bond, bricks should be placed by marking their grooves facing upward.
- In case of concrete block
- Concrete blocks should be placed so that the rough faces point towards top and bottom to get an excellent bond.
- The strength of blocks must be good enough.
- Brush the bottom and leading faces prior to laying.
Avoid wall thickness exceeding 450 mm, and limit the length of the wall to 6 m. The horizontal walls make masonry more efficient. It is best to build partitions along the main wall, and two walls must be installed.
- Window and Doors Openings:
- Walls with a lot of windows and doors ear each other collapse early.
- Window should be kept at the same level.
- The overall width of all openings in the wall must not go beyond one-third length of the wall
- Doors must not be positioned at the end of the wall. They should be provided at a distance of at least 400to 500 mm from the cross wall.
- Clear width in between two openings must not be less than 600mm.
- Roofing:
In sloping roofing systems with longer span higher than 6m, use trusses rather than rafters. Structure with a four-sided sloping roofing system, considering that gable walls collapse early.
- Chajjas:
Limit chajjas or terrace projections to 0.9 – 1m. For bigger projections, always use columns and beams for their support in earthquake-resistant buildings.
- Parapet:
Masonry parapet walls easily collapse due to earthquakes. It is much better to construct a parapet with bricks approximately 300 mm in thickness, followed by iron railings.
- Retrofitting:
During the renovation process, the structure should be prepared in such a way that all elements of the building function as a single system. Generally, this is the fastest and most economical way to fix the structure. Following are few of the approaches in retrofitting:
- Anchor roofing truss to walls with brackets
- Purlins and bottom chord member of trusses should be connected by bracings.
- The strength of gable wall should be increased by placing sloping belt on gable wall.
- Corners of the buildings should be strengthened with seismic belts.
- Floor joist should be anchored to walls with brackets.
- Vertical reinforcement should be provided to increase the connection capacity of each story.
- Vertical reinforcement should be provided in all (inside and outside) corners of the building to reduce the tensile stress caused due to vertical bending of walls.
- Encase wall openings with reinforcement.